Scenario di laboratorio: Routing dinamico con OSPF
Cisco Packet Tracer – 4 router, 4 LAN, rete di transito e Area 0
Configura OSPF (Link-State), verifica le adiacenze e controlla le rotte
O in tabella di routing.
Scenario e obiettivi (OSPF)
Idea chiave: OSPF è un protocollo Link-State. I router
costruiscono una
mappa della topologia (LSDB) scambiando LSA, poi calcolano i
percorsi migliori con
l’algoritmo SPF (Dijkstra). La metrica è il cost (basato sulla
bandwidth dell’interfaccia).
Differenza rispetto a RIP: RIP scambia “distanze” (hop count) periodicamente.
OSPF invece sincronizza la topologia e converge più velocemente, risultando più scalabile e adatto a
reti reali.
In questo laboratorio costruiamo un dominio OSPF in Area 0 con 4 router collegati
tra loro tramite
reti di transito (/27) e con 4 LAN utente (/24).
Obiettivo operativo: dopo la configurazione OSPF, ogni router deve:
- formare le adiacenze (neighbor) con i router collegati;
- apprendere automaticamente tutte le reti remote;
- mostrare rotte O in
show ip routee permettere ping end-to-end tra le LAN.
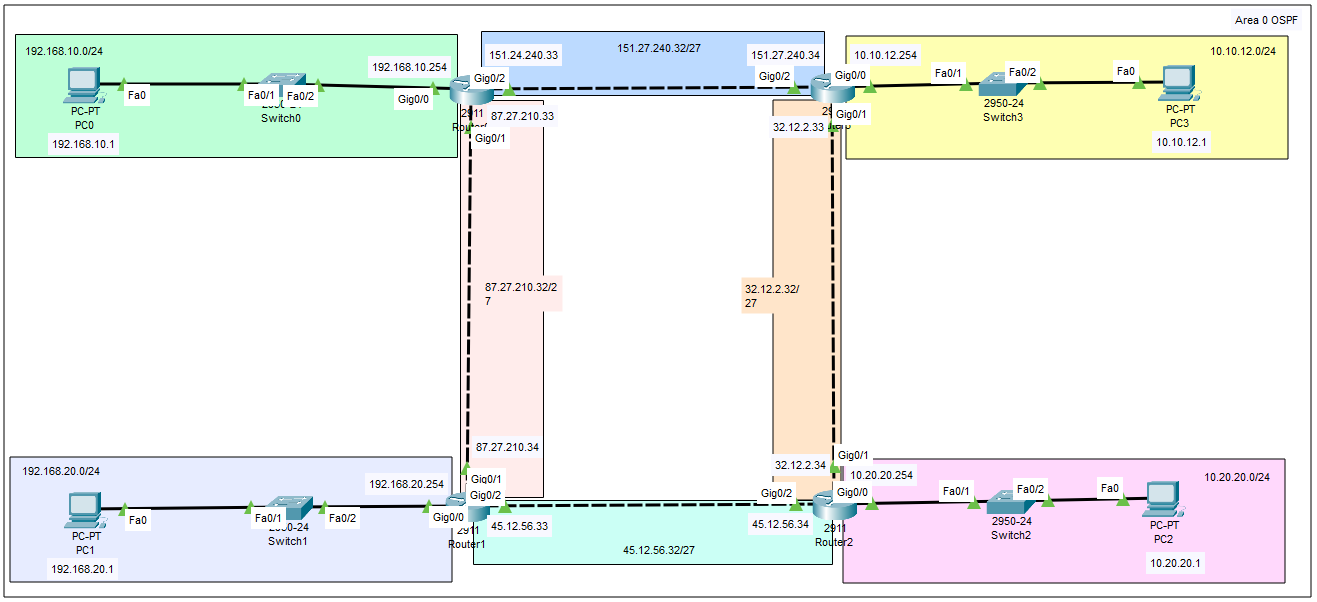
Topologia e piano di indirizzamento
La topologia prevede 4 LAN /24 e 4 collegamenti di transito /27 (wildcard OSPF
0.0.0.31).
I router usano interfacce GigabitEthernet.
| Elemento | Rete | Note |
|---|---|---|
| LAN Router0 | 192.168.10.0/24 |
Gateway tipico 192.168.10.254 |
| LAN Router1 | 192.168.20.0/24 |
Gateway tipico 192.168.20.254 |
| LAN Router2 | 10.20.20.0/24 |
Gateway tipico 10.20.20.254 |
| LAN Router3 | 10.10.12.0/24 |
Gateway tipico 10.10.12.254 |
| Transito R0↔R1 | 87.27.210.32/27 |
host tipici .33 e .34 |
| Transito R0↔R3 | 151.27.240.32/27 |
host tipici .33 e .34 |
| Transito R1↔R2 | 45.12.56.32/27 |
host tipici .33 e .34 |
| Transito R3↔R2 | 32.12.2.32/27 |
host tipici .33 e .34 |
Gateway dei PC: ogni PC deve avere come default gateway l’IP del router nella
propria LAN
(es.
192.168.10.254, 192.168.20.254, 10.20.20.254,
10.10.12.254).
Prima di OSPF: controlla che tutte le interfacce siano up/up e che
i router
pinghino i vicini sulle reti di transito. OSPF forma l’adiacenza solo se il link è operativo.
Nota didattica: nel comando OSPF
network si usa la coppia
rete + wildcard mask (non la subnet mask). Esempio: per una /27 la wildcard è
0.0.0.31.
Configurazione OSPF sui router (Packet Tracer)
Logica: abilita OSPF (process-id
10) e inserisci le reti da pubblicare
in Area 0.
Le interfacce che “matchano” i comandi network entreranno nel dominio OSPF e tenteranno
di formare neighbor.
Punto cruciale: se sbagli la wildcard o la rete, l’interfaccia non entra in OSPF e
non si forma l’adiacenza.
Comando di controllo:
show ip ospf interface brief e
show ip ospf neighbor.
Router0
enable
conf t
router ospf 10
network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 87.27.210.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
network 151.27.240.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
end
wr
Controllo: Router0 deve partecipare a OSPF sulla LAN
192.168.10.0/24
e su due reti di transito /27.
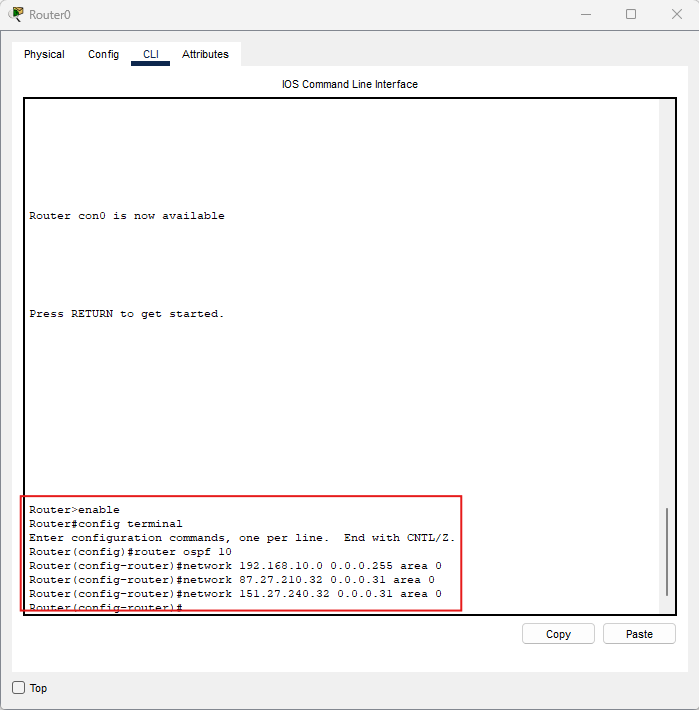
Immagine: comandi OSPF su Router0.
Router1
enable
conf t
router ospf 10
network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 45.12.56.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
network 87.27.210.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
end
wr
Controllo: Router1 collega la LAN
192.168.20.0/24 a
due transiti /27
(verso Router0 e Router2).
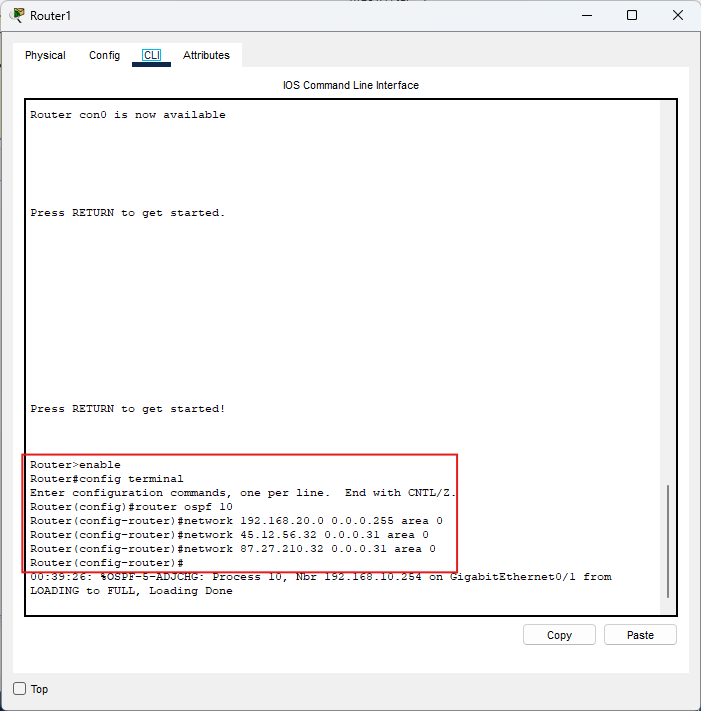
Immagine: comandi OSPF su Router1.
Router2
enable
conf t
router ospf 10
network 10.20.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 32.12.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
network 45.12.56.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
end
wr
Controllo: Router2 pubblica la LAN
10.20.20.0/24 e i
transiti /27
verso Router1 e Router3.
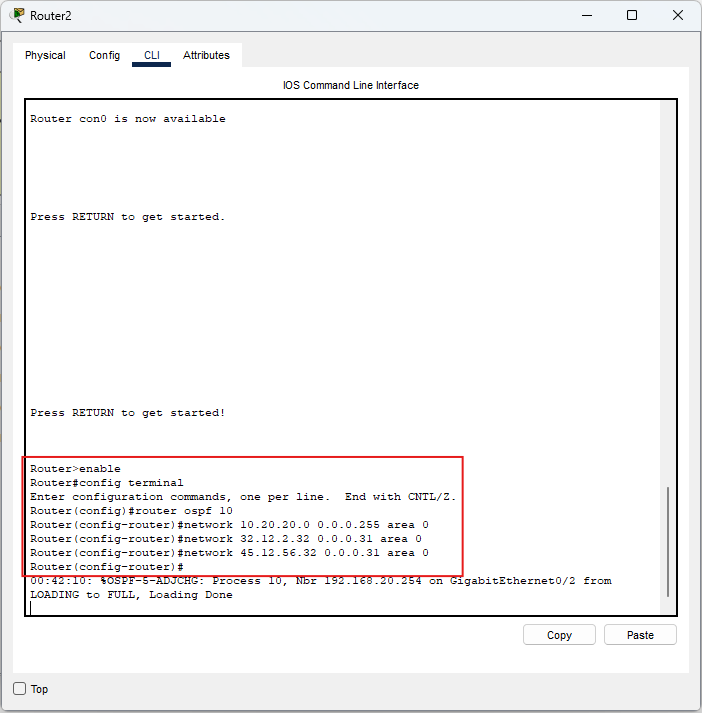
Immagine: comandi OSPF su Router2.
Router3
enable
conf t
router ospf 10
network 10.10.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 32.12.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
network 151.27.240.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
end
wr
Controllo: Router3 pubblica la LAN
10.10.12.0/24 e i
transiti /27
verso Router0 e Router2.
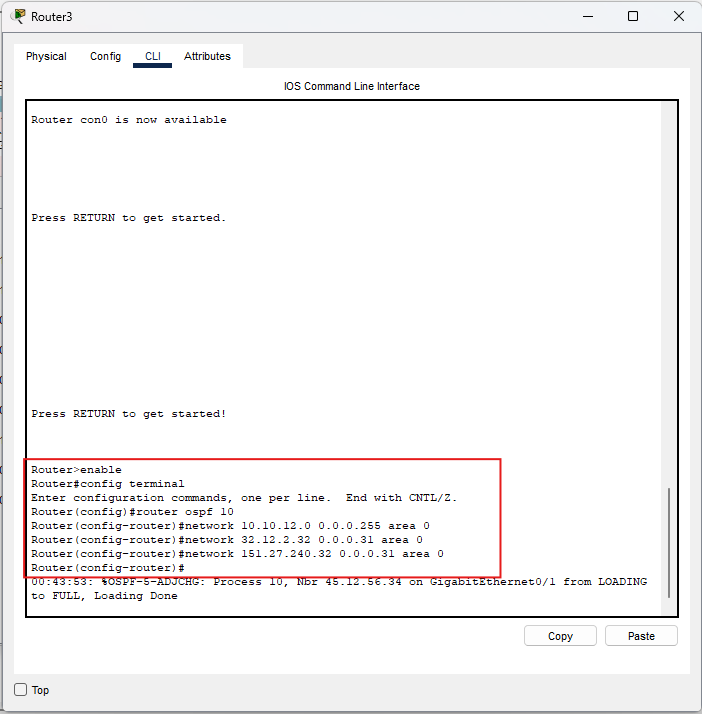
Immagine: comandi OSPF su Router3.
Verifica adiacenze (fondamentale):
show ip ospf neighbor→ i neighbor devono risultare in stato FULLshow ip ospf interface brief→ interfacce incluse in OSPF e area
Verifica e interpretazione delle rotte (show ip route)
Prima di OSPF: la tabella di routing contiene solo rotte C
(Connected) e L (Local).
Dopo OSPF devono comparire rotte O verso le reti remote.
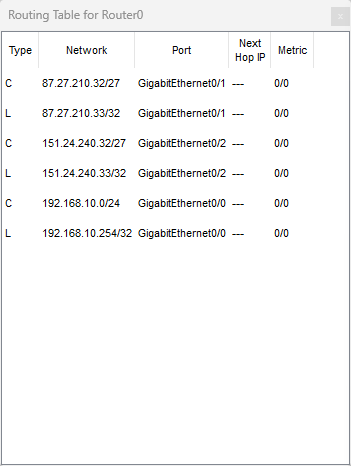
Router0 (prima)
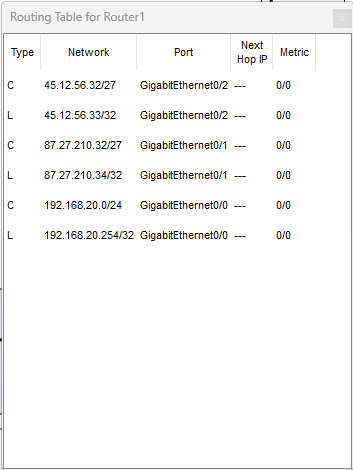
Router1 (prima)
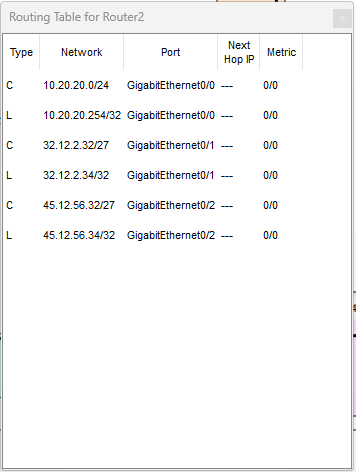
Router2 (prima)
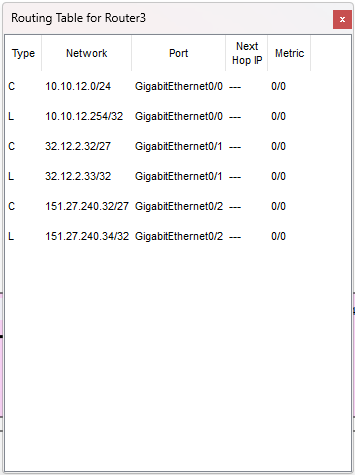
Router3 (prima)
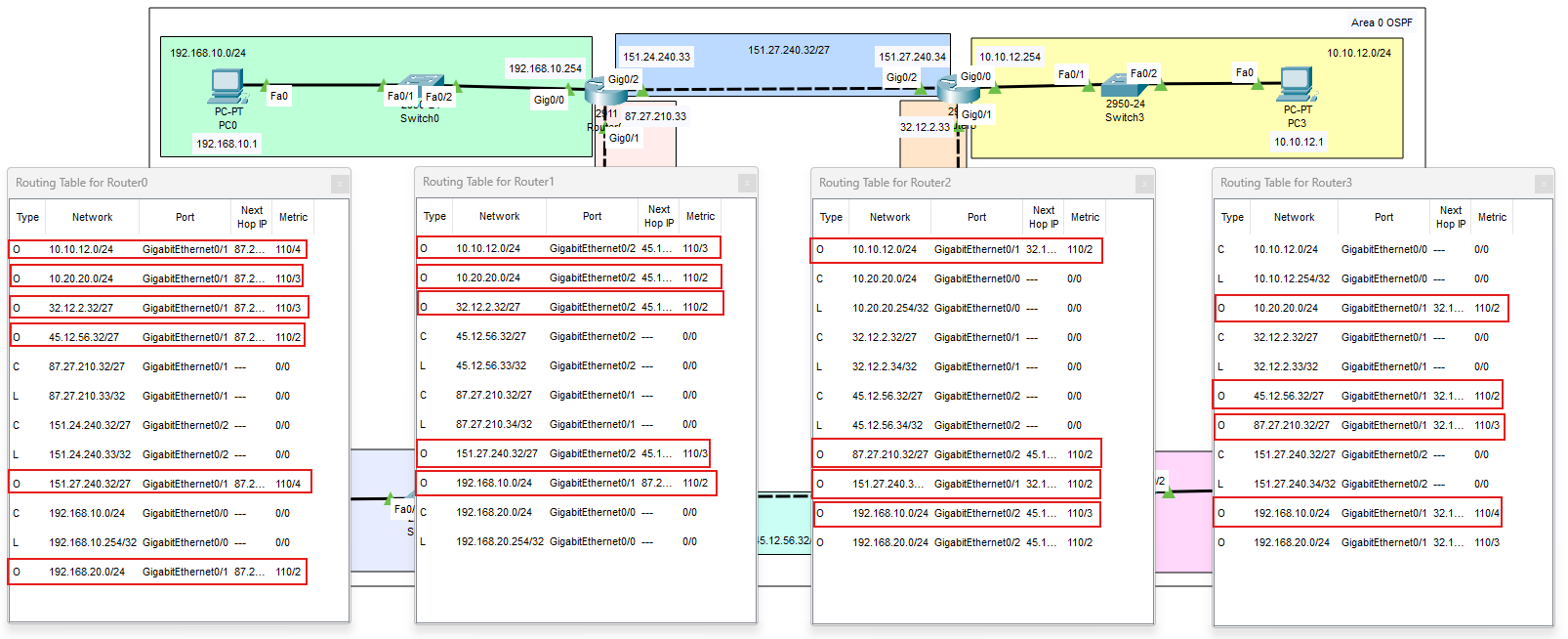
Come leggere una rotta OSPF
Esempio:
O 10.10.12.0/24 [110/4] via 87.27.210.34
- O = route appresa via OSPF (intra-area)
- 110 = Administrative Distance di OSPF
- 4 = cost (metrica OSPF, dipende dalle interfacce attraversate)
- via = next-hop verso la destinazione
Comandi indispensabili:
show ip route→ verifica rotte O e next-hopshow ip ospf neighbor→ neighbor in stato FULLshow ip protocols→ riepilogo routing e processishow run | section router ospf→ controlla lenetwork ... area 0
Test end-to-end: esegui ping tra PC di LAN diverse:
- da
192.168.10.xverso10.20.20.x - da
192.168.20.xverso10.10.12.x
Troubleshooting essenziale (OSPF):
- Neighbor non in FULL: verifica che siano sulla stessa rete L2, stessa area e che le interfacce siano up.
- Wildcard errata: l’interfaccia non entra in OSPF → ricontrolla
network ... wildcard area 0. - Gateway PC errato: deve essere l’IP del router nella LAN.
- Se le rotte non compaiono: prima risolvi le adiacenze (
show ip ospf neighbor), poi ricontrolla la routing table.
Riepilogo rapido
- OSPF è Link-State: LSDB + SPF (Dijkstra) → convergenza più rapida rispetto a RIP.
- Configurazione base:
router ospf 10+network rete wildcard area 0. - Verifica prioritaria:
show ip ospf neighbor→ i neighbor devono risultare FULL. - In tabella di routing: le rotte OSPF compaiono come O con AD 110.
- Errori tipici: wildcard sbagliata, interfaccia down, gateway PC errato, adiacenze non formate.