Scenario di laboratorio: Routing dinamico con RIPv1
Cisco Packet Tracer – 3 router, 3 LAN, 2 link seriali /30
Configura RIP v1, verifica l’apprendimento delle rotte e testa la connettività
end-to-end.
Scenario e obiettivi (RIPv1)
Idea chiave: RIP è un protocollo Distance Vector. Ogni router
scambia periodicamente
con i vicini un insieme di rotte apprese; la metrica è il numero di hop (massimo
15: oltre è “infinito”).
Attenzione (didattica): RIPv1 è classful (non trasporta la subnet
mask negli aggiornamenti).
Questo significa che:
- non è adatto a VLSM e scenari con subnet mask diverse all’interno dello stesso “major network”;
- può creare problemi di summarization/ambiguità in reti più complesse.
In questo laboratorio costruiamo una rete “lineare” con 3 router: Router0 ↔ Router1 ↔ Router2. Ogni router ha una LAN locale (classe C privata), mentre i collegamenti tra router sono link seriali in /30.
Obiettivo operativo: dopo la configurazione RIP, ogni router deve imparare
automaticamente le LAN remote.
I PC devono potersi pingare tra LAN diverse (es.
192.168.0.1 →
192.168.2.1).
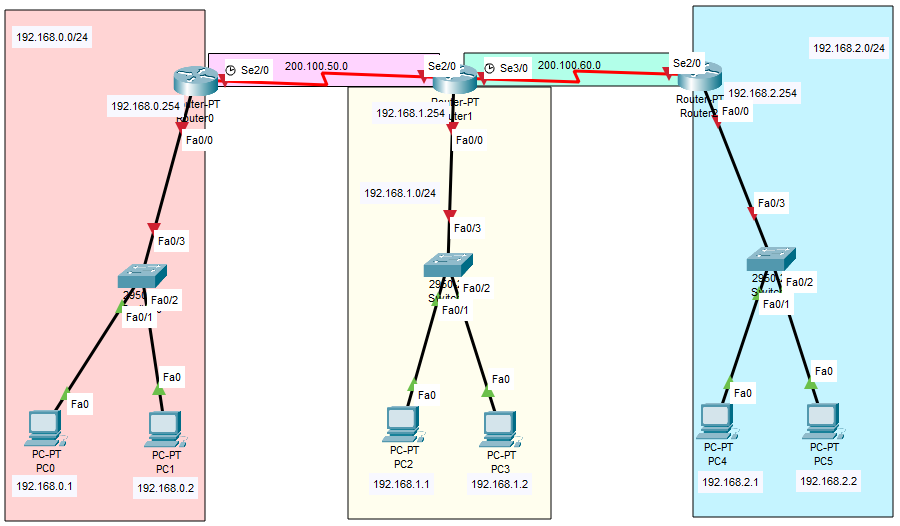
Topologia e piano di indirizzamento
La topologia usa tre LAN /24 e due collegamenti seriali /30:
| Elemento | Rete | Uso |
|---|---|---|
| LAN Router0 | 192.168.0.0/24 |
PC0, PC1 – gateway 192.168.0.254 |
| LAN Router1 | 192.168.1.0/24 |
PC2, PC3 – gateway 192.168.1.254 |
| LAN Router2 | 192.168.2.0/24 |
PC4, PC5 – gateway 192.168.2.254 |
| Seriale R0↔R1 | 200.100.50.0/30 |
punto-punto (2 host) |
| Seriale R1↔R2 | 200.100.60.0/30 |
punto-punto (2 host) |
Gateway dei PC: ogni PC deve avere come default gateway l’IP del router nella
stessa LAN (es. LAN0 →
192.168.0.254).
Un gateway errato è la causa più comune di ping falliti.
Prima di RIP: verifica che tutte le interfacce siano up/up e
che i router
“si vedano” sui link seriali (ping tra gli IP delle seriali). Se una seriale è down, RIP non
annuncia quella rete.
Nota sui comandi RIP: nel comando
network è didatticamente corretto
usare l’indirizzo di rete
(es. 192.168.0.0) e non un IP host (es. 192.168.0.2), anche se in alcuni
simulatori può “passare lo stesso”.
Configurazione RIPv1 sui router (Packet Tracer)
Logica: su ogni router abiliti RIP e indichi quali reti direttamente connesse
devono essere annunciate.
RIP invierà aggiornamenti ai router vicini sulle interfacce che appartengono a quelle reti.
Router0
enable
conf t
router rip
network 192.168.0.0
network 200.100.50.0
end
wr
Controllo: Router0 deve annunciare la LAN
192.168.0.0/24 e il link 200.100.50.0/30.
Se dimentichi la seriale, Router1 non riceve gli update.
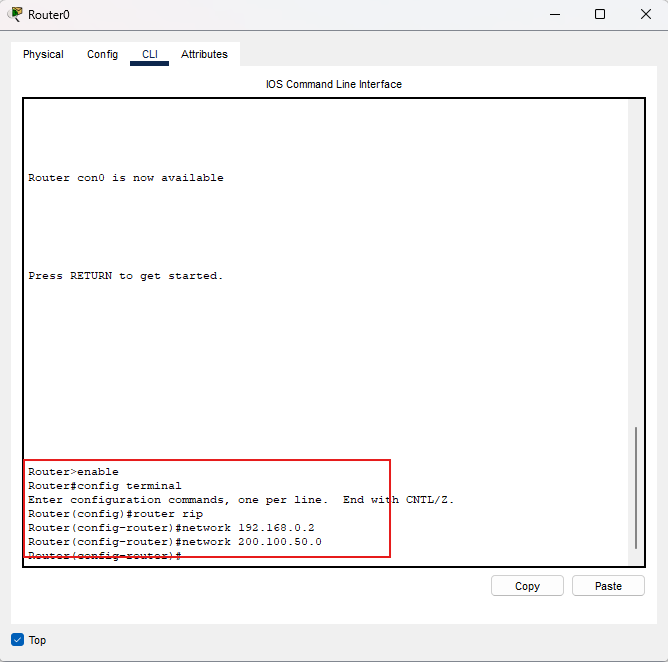
Immagine: comandi RIP su Router0.
Router1 (centrale)
enable
conf t
router rip
network 192.168.1.0
network 200.100.50.0
network 200.100.60.0
end
wr
Ruolo di Router1: collega i due domini seriali. Qui l’errore tipico
è
dimenticare
200.100.60.0 oppure 200.100.50.0.
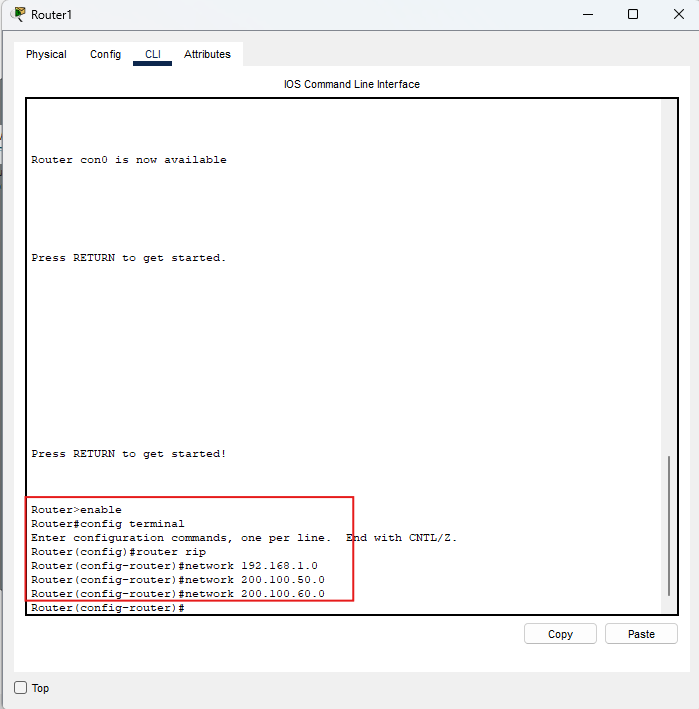
Immagine: comandi RIP su Router1.
Router2
enable
conf t
router rip
network 192.168.2.0
network 200.100.60.0
end
wr
Controllo: Router2 deve annunciare la LAN
192.168.2.0/24 e il link 200.100.60.0/30.
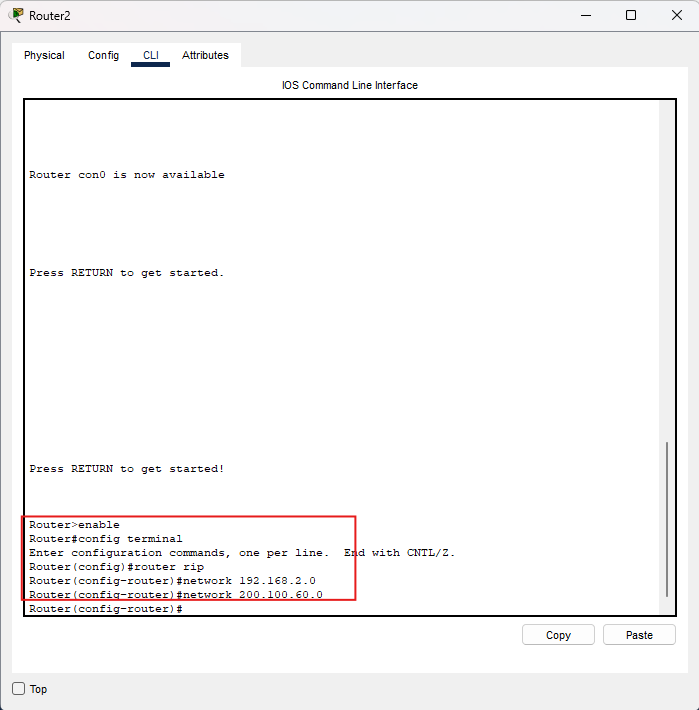
Immagine: comandi RIP su Router2.
Convergenza: dopo l’attivazione, attendi qualche secondo. In Packet Tracer
l’apprendimento può non essere “istantaneo”.
Se vuoi forzare un aggiornamento, puoi fare un ping tra router su seriale e poi ricontrollare
show ip route.
Verifica e interpretazione delle rotte (show ip route)
Prima di RIP: la tabella di routing contiene solo rotte C
(Connected), cioè reti direttamente collegate.
Dopo RIP devono comparire rotte R verso le reti remote.
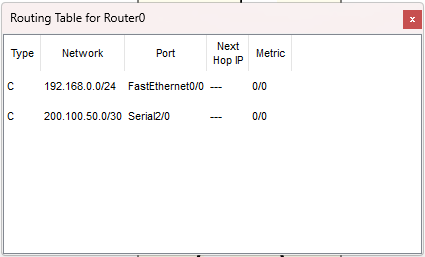
Router0 (prima)
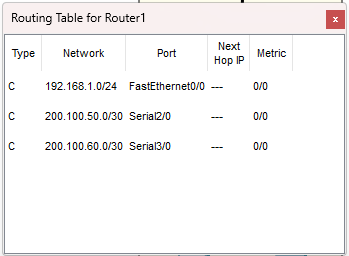
Router1 (prima)
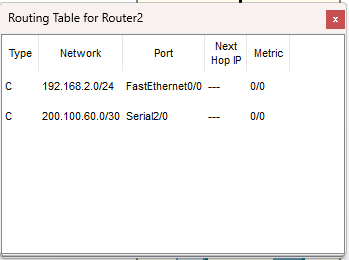
Router2 (prima)
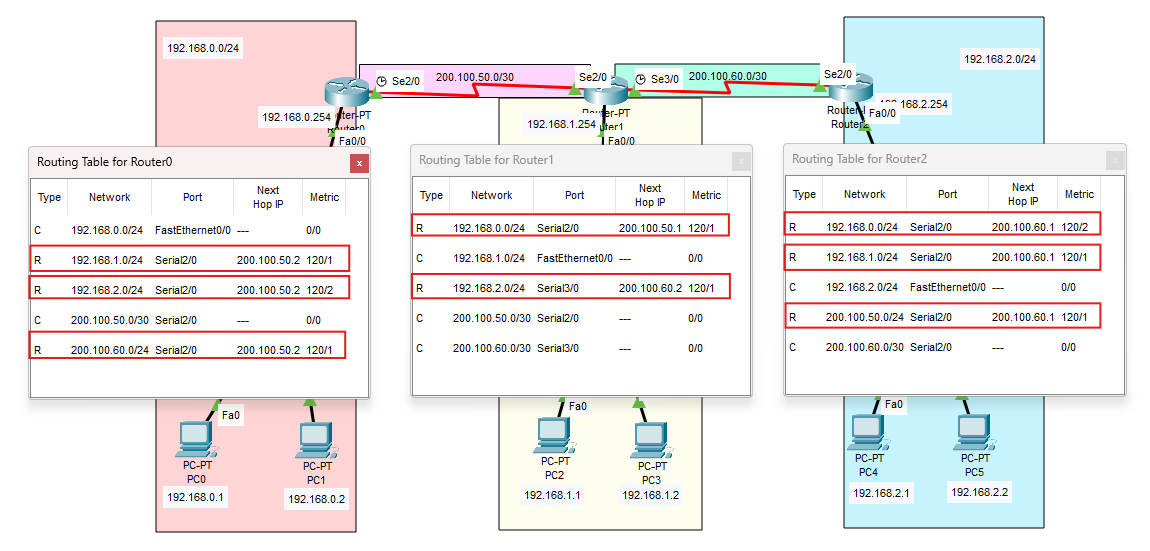
Come leggere una rotta RIP
Esempio:
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/2] via 200.100.50.2
- R = appresa tramite RIP
- 120 = Administrative Distance (RIP)
- 2 = metrica (hop count)
- via = next-hop (router successivo)
Comandi indispensabili:
show ip route→ verifica rotte R e next-hopshow ip protocols→ verifica reti annunciate e timer RIPshow run | section router rip→ controlla rapidamente inetwork
Test end-to-end: esegui ping tra PC di LAN diverse:
- da
192.168.0.1verso192.168.2.1 - da
192.168.2.2verso192.168.1.1
Troubleshooting essenziale (se non vedi rotte RIP):
- Interfaccia down: verifica
show ip int brief(stato up/up) e cavi seriali/DCE. - Rete non annunciata: verifica la sezione RIP con
show run | section router rip. - IP/mask errati sui link /30: ricontrolla che siano nello stesso /30 ai due estremi.
- Gateway PC errato: deve essere l’IP del router in LAN (es.
192.168.x.254).
Riepilogo rapido
- RIPv1 è un protocollo Distance Vector con metrica hop count (max 15).
- È classful: non trasporta la subnet mask → non adatto a VLSM e reti complesse.
- Config:
router rip+networkdelle reti direttamente connesse. - Verifica:
show ip route(rotte R),show ip protocols, ping end-to-end. - Errori tipici: link down, rete mancante nei
network, gateway PC errato, /30 configurate male.